Okay, let’s be real. Talking about interest rates and mortgage rates can feel like wading through alphabet soup. Prime rates, federal funds rate, 10-year Treasury yield… it’s enough to make your head spin. But here’s the thing: understanding this stuff isn’t just for economists or Wall Street gurus. It directly impacts your wallet, your dreams of owning a home, and even the overall health of the economy. So, let’s ditch the jargon and dive into what’s really happening, and why it matters to you.
The Fed’s Hand: Why Interest Rates Matter
The Federal Reserve, or “the Fed,” is the central bank of the United States. They’re the puppet masters, if you will, pulling the strings on interest rates . Their primary tool is the federal funds rate, which is the rate at which banks lend money to each other overnight. Now, you might be thinking, “Okay, great, but how does that affect me?” Well, the federal funds rate serves as a benchmark for many other interest rates , including those for credit cards, auto loans, and, you guessed it, mortgage rates .
When the Fed raises interest rates , it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money. They, in turn, pass those costs onto consumers in the form of higher interest rates . This can slow down economic growth because people and businesses are less likely to borrow money to spend and invest. On the flip side, when the Fed lowers interest rates , borrowing becomes cheaper, which can stimulate the economy. Alphabet Stock Price Why does the Fed do this dance? Their goal is to maintain price stability (keep inflation in check) and promote full employment. It’s a delicate balancing act, and they don’t always get it right.
Mortgage Rates: Your Ticket to Homeownership (or Not)
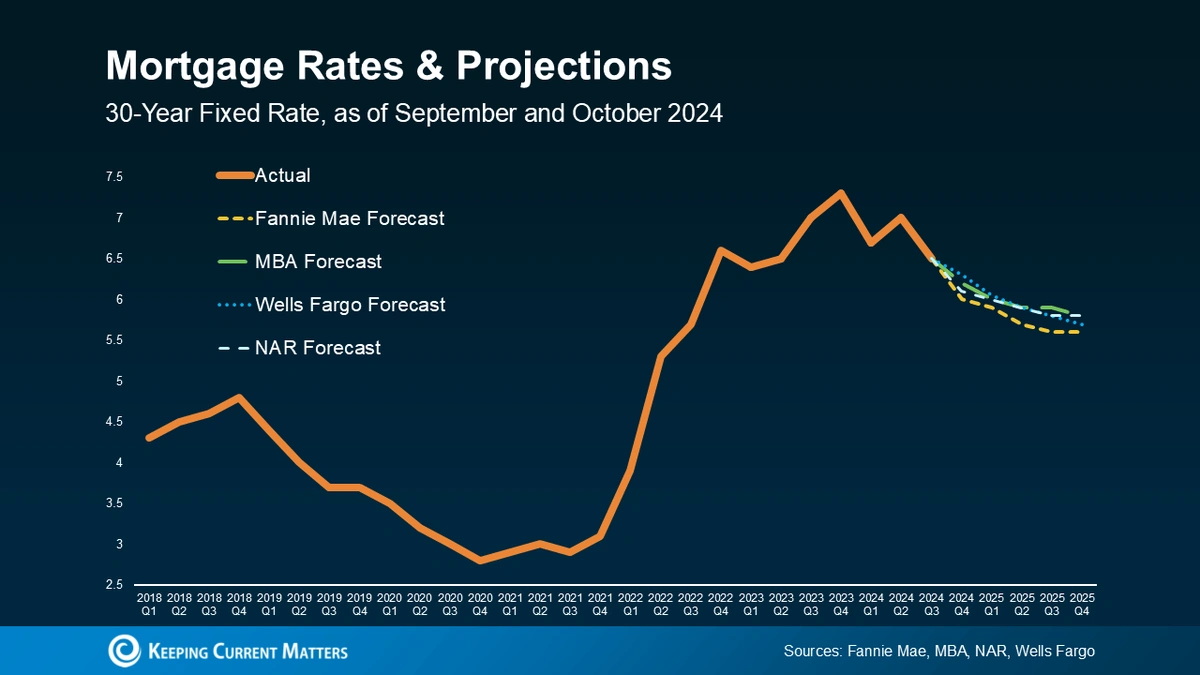
Ah, mortgage rates . The bane of many a first-time homebuyer’s existence. These rates, which determine the cost of borrowing money to buy a home, are heavily influenced by the 10-year Treasury yield. This yield reflects investors’ expectations for future inflation and economic growth. When the 10-year Treasury yield rises, mortgage rates typically follow suit, and vice versa.
Here’s the thing about mortgage rates : even small fluctuations can have a huge impact on your monthly payment and the total amount you’ll pay over the life of the loan. Let’s say you’re looking at a $300,000 mortgage. A 0.5% increase in the interest rate could add tens of thousands of dollars to your total cost. Crazy, right? That’s why it’s crucial to shop around for the best rate and understand the terms of your loan. (More on that later.)
Fixed vs. Adjustable | Choosing the Right Path
So, you’ve decided to take the plunge and buy a home. Congratulations! Now comes the next big decision: fixed-rate or adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM)? A fixed-rate mortgage means your interest rate stays the same for the entire loan term, typically 15 or 30 years. This provides stability and predictability, which can be a big plus for budgeting. An ARM, on the other hand, has an interest rate that can change over time, usually based on a benchmark rate like the prime rate. ARMs often start with lower interest rates than fixed-rate mortgages, but they can increase significantly if rates rise. If you are interested in technology and computing, see Unlocking Shell Command Line
Which one is right for you? It depends on your risk tolerance, your financial situation, and your expectations for future interest rates . If you plan to stay in the home for a long time and value stability, a fixed-rate mortgage might be the way to go. If you only plan to stay for a few years and are comfortable with some risk, an ARM could save you money in the short term. It’s worth noting that understanding prime rates can also influence this decision.
Navigating the Market | Tips for Borrowers
Okay, so how do you navigate this complicated world of interest rates and mortgage rates ? Here are a few tips:
- Shop around: Don’t just go with the first lender you find. Get quotes from multiple lenders and compare rates, fees, and terms.
- Improve your credit score: A higher credit score typically means a lower interest rate. Pay your bills on time, keep your credit card balances low, and avoid opening too many new accounts.
- Save for a larger down payment: A larger down payment means you’ll borrow less money, which can translate to a lower interest rate and lower monthly payments.
- Consider a shorter loan term: A 15-year mortgage typically has a lower interest rate than a 30-year mortgage. You’ll pay off the loan faster and save money on interest in the long run, but your monthly payments will be higher.
- Work with a mortgage broker: A mortgage broker can help you find the best loan for your situation and negotiate with lenders on your behalf.
By exploring different options like conventional mortgages and understanding the impact of inflation , you can make more informed decisions.
The Big Picture | What Does It All Mean?
Ultimately, the relationship between interest rates and mortgage rates is a complex one. Changes in rates can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, impacting everything from consumer spending to business investment to the housing market. As of late 2023, the Federal Reserve has paused raising interest rates .According to the Federal Reserve’s website, the decision to pause was made to allow time to assess the effects of previous rate hikes and incoming economic data. The target range for the federal funds rate remains at 5.25% – 5.50%. This is great news for some people who are looking to buy a home with a low fixed rate.
Understanding this dynamic can help you make informed financial decisions and navigate the ever-changing economic landscape. And hey, maybe you can even impress your friends at your next dinner party with your newfound knowledge of monetary policy ! What fascinates me is that even though the market seems daunting, a little bit of understanding can go a long way. Let’s be honest, it is all a little daunting at first! But it’s something we can all figure out together.
FAQ: Interest Rates and Mortgage Rates
What’s the difference between the federal funds rate and the prime rate?
The federal funds rate is the rate at which banks lend money to each other overnight, while the prime rate is the rate that banks charge their most creditworthy customers. The prime rate is typically about 3 percentage points higher than the federal funds rate.
How do economic indicators influence mortgage rates?
Economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, and employment data can all influence mortgage rates . Strong economic growth and rising inflation typically lead to higher mortgage rates .
What if I have a low credit score? Will that affect my mortgage rate?
Yes, a low credit score will likely result in a higher mortgage rate . Lenders see borrowers with low credit scores as riskier, so they charge higher rates to compensate.
Can I refinance my mortgage if interest rates go down?
Yes, you can refinance your mortgage if interest rates go down. Refinancing involves taking out a new mortgage to pay off your old one. If you can get a lower interest rate on the new mortgage, you can save money on your monthly payments and over the life of the loan.
How often do mortgage rates change?
Mortgage rates can change multiple times a day, depending on market conditions. It’s important to stay informed and monitor rates closely if you’re planning to buy a home or refinance your mortgage. Keep an eye on the latest market trends to anticipate potential fluctuations.
In conclusion, navigating the landscape of interest rates and mortgage rates requires more than just knowing the numbers; it’s about understanding the underlying dynamics and making informed decisions that align with your financial goals.




