Imagine this: You’re sipping your morning chai, scrolling through the news, and BAM! Headlines scream about Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) winning the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Cool, right? But… what are MOFs, and why should someone in India, whether you’re a student, researcher, or just a curious soul, even care? Here’s the thing: it’s not just about some fancy award; it’s about a technology that could change the way we live, breathe, and power our world. So, let’s dive deep beyond the headlines, shall we?
The “Why” | Unpacking the Significance of MOFs
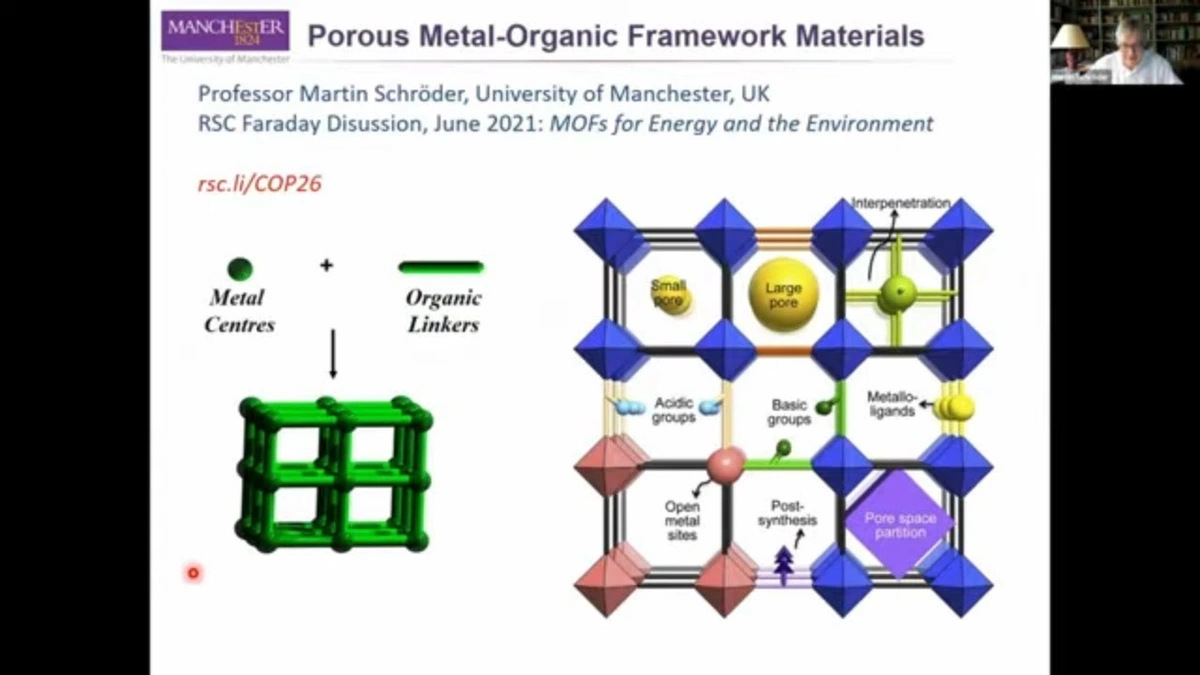
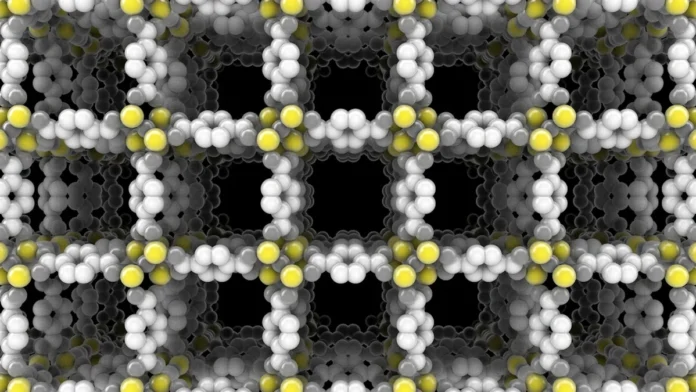
Okay, let’s be honest – the name “Metal-Organic Frameworks” sounds intimidating. But break it down, and it becomes fascinating. These are basically tiny, incredibly porous structures – think of them as microscopic sponges built from metal ions and organic molecules. The magic lies in their surface area; a single gram of MOF can have a surface area equivalent to a football field! But why is that surface area such a critical aspect ? Well, it allows them to trap, store, and separate gases and liquids with unparalleled efficiency. But, so, here’s why India should pay attention.
India, like many developing nations, faces immense challenges in areas like clean energy, water purification, and pollution control. MOFs offer potentially game-changing solutions. For example, they can be used to capture carbon dioxide from power plants, helping to mitigate climate change. They can also be used to store hydrogen for fuel cells, paving the way for a cleaner transportation sector. And, perhaps most critically, they can filter out pollutants from water, providing access to clean drinking water for millions. What fascinates me is the potential for these MOFs to indigenously solve some of India’s most persistent problems.
How MOFs are Developed
Let’s get practical. How does one actually make a MOF? The process, at its core, is about self-assembly. Scientists carefully select metal ions and organic linkers, then coax them to connect in a specific, repeating pattern. It’s like building with Lego bricks on a molecular level – but instead of plastic, you’re using atoms! A common mistake I see people make is assuming that all MOFs are created equal. In reality, the properties of a MOF are highly dependent on the choice of metal and organic components, as well as the synthesis conditions. This means researchers have immense flexibility to tailor MOFs for specific applications.
And, because material science is constantly evolving, the development of MOFs requires advanced methodologies . The most common synthetic methodologies include, but are not limited to, solvothermal and ionothermal synthesis, microwave and electrochemical synthesis, mechanochemical and sonochemical synthesis, and layer-by-layer assembly.
Research and development in this area are exploding, and a significant amount of that is happening right here in India. Indian scientists are at the forefront of developing novel MOFs for applications ranging from gas storage to drug delivery. I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized the real hurdle is scaling up production. That’s where the 2025 Nobel Prize comes in – it validates the field and attracts even more investment and talent.
The Emotional Angle | Hope and the Future of Sustainability
Okay, let’s talk about hope. In a world grappling with climate change and environmental degradation, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But the story of MOFs is a story of human ingenuity and the power of science to create solutions. According to the latest circular on the official Department of Science and Technology website ( dst.gov.in ), the Indian government is heavily investing in nanotechnology and advanced materials research, including MOFs. This signals a commitment to finding innovative solutions to India’s pressing challenges. What fascinates me is that the journey is not merely about the technology, but about the people behind it. Scientists driven by a passion to make a difference, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. These scientists understand that their work contributes to a global effort.
That moment when a scientist discovers a new MOF with unprecedented gas adsorption properties – that’s a moment of pure inspiration. Let’s walk through this together, step-by-step, so you can get back to focusing on what really matters: a future where technology and nature coexist harmoniously.
The Potential Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks
MOFs have a wide range of potential applications. As mentioned earlier, one of the most important is carbon capture . This is when carbon dioxide is removed from flue gases at power plants and stored underground. This could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. MOFs can also be used to store fuels such as hydrogen and methane. Hydrogen is a clean-burning fuel that could power vehicles and generate electricity. However, hydrogen is difficult to store because it is a very light gas. MOFs can trap and release gases, allowing for safe and efficient storage. As per the guidelines mentioned in the information bulletin , MOFs are also effective in water purification. Here is more about science .
MOFs are also being investigated for use in drug delivery. Drugs can be encapsulated within the pores of MOFs and then released in a controlled manner. This could improve the effectiveness of drugs and reduce side effects. Another thing I’ve found fascinating is that the one thing you absolutely must double-check is that the MOFs are non-toxic. MOFs are being explored for use in sensors. The electrical properties of MOFs change when they adsorb gases or liquids. This makes them ideal for use in sensors that can detect pollutants or other chemicals.
Future Directions and Challenges
Of course, there are challenges. Scaling up the production of MOFs to industrial levels is a major hurdle. We need to find cost-effective and sustainable ways to manufacture these materials. Another challenge is improving the stability of MOFs. Some MOFs are sensitive to moisture or air, which limits their applications. What’s more, as space exploration increases, MOFs can be developed for use in outer space.
But the potential rewards are enormous. Imagine a world powered by clean energy, where pollution is a thing of the past, and where access to clean water is a reality for everyone. MOFs may be the key to unlocking that future. And India, with its vibrant scientific community and its commitment to sustainable development, is poised to play a leading role in this revolution. According to research by the Indian Institute of Science, customized MOFs can be produced. Let me rephrase that for clarity: India could be at the forefront of groundbreaking scientific developments!
FAQ About Metal-Organic Frameworks
What exactly are Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs)?
MOFs are highly porous materials made of metal ions and organic molecules, known for their incredibly large surface areas.
How can MOFs help with climate change?
They can capture carbon dioxide from power plants, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Are MOFs being developed in India?
Yes, Indian scientists are actively researching and developing MOFs for various applications.
Can MOFs purify water?
Yes, they can filter out pollutants, providing access to clean drinking water.
What are some of the challenges in using MOFs?
Scaling up production and improving their stability are major challenges.
Where can I find more information about the use of MOFs?
You can find information on the official government website (e.g. dst.gov.in) or academic journals such as Nature.
So, the next time you hear about Metal-Organic Frameworks, remember it’s not just a science story, it’s an India story. It’s a story about innovation, sustainability, and the unwavering pursuit of a better future. And that, my friend, is something worth getting excited about. MOF applications are only just being discovered.