Okay, let’s talk about something that sounds like it’s straight out of a sci-fi movie: the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). Now, you might be thinking, “Anomaly? Sounds ominous!” And well, it kind of is, especially when you hear that it’s expanding, as new data from the European Space Agency’s Swarm satellites suggests. But before you start picturing doomsday scenarios, let’s break down what this actually means, why it matters to us in India (yes, even us!), and what implications it might have. Think of it as the Earth having a bit of a hiccup – a geomagnetic hiccup, to be precise.
What Exactly IS the South Atlantic Anomaly?
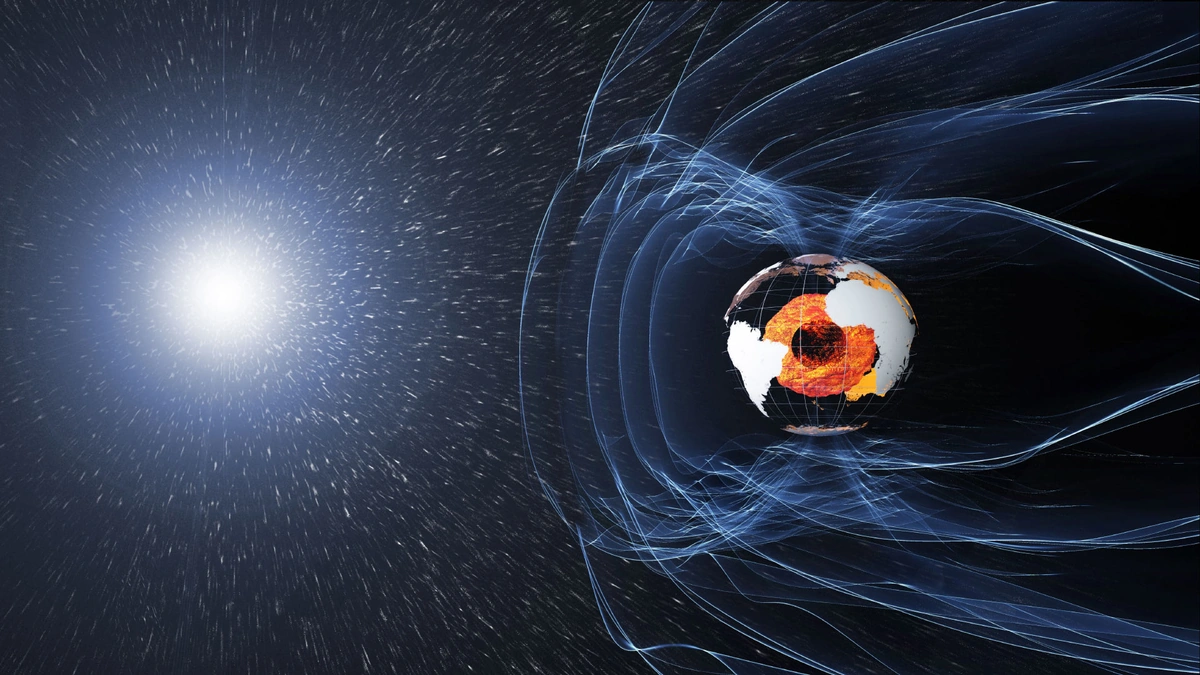
Here’s the thing: Earth has a magnetic field, right? It’s like our planet’s invisible shield, protecting us from harmful solar radiation. This field isn’t uniform; it varies in strength across the globe. The SAA is essentially a region where this magnetic field is particularly weak. It’s centered over South America and a portion of the South Atlantic Ocean (hence the name). But, as the title suggests, the South Atlantic Anomaly expansion is what’s got scientists buzzing.
Think of it like this: imagine you’re holding a magnet, and in one particular spot, the magnetic force just…fizzles out a bit. That’s the SAA. Now, why does this happen? Well, the Earth’s magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron in its outer core – a process called the geodynamo. The SAA is thought to be a consequence of the complex and somewhat chaotic nature of this geodynamo. There are areas where the Earth’s inner workings create dips in the magnetic field. This is why understanding the geomagnetic field is so critical.
Why Should We Care About a Weak Spot in the Magnetic Field?
Right, so, a weak magnetic field – big deal, right? Actually, it kind of is. When the magnetic field is weaker, it offers less protection from charged particles coming from the sun. And that’s where things get interesting. These charged particles can mess with satellites orbiting the Earth. Satellites passing through the SAA are exposed to higher levels of radiation, which can cause malfunctions and data loss. This is a huge issue for communication satellites, weather satellites, and even the International Space Station, which all regularly pass through this region. Plus, the magnetic field strength directly impacts how technology functions in space. Let’s be honest, a satellite hiccup halfway across the globe can indirectly affect weather forecasting, GPS navigation, and even your daily dose of internet!
But, and this is important, it’s not just about satellites. Increased radiation can also affect high-altitude flights. While the atmosphere still provides a buffer, pilots and passengers on long-haul flights over the SAA region might be exposed to slightly higher levels of radiation. So, what do these ESA Swarm satellite do? The Swarm mission is dedicated to studying the Earth’s magnetic field and its variations. These satellites provide incredibly precise measurements of the magnetic field, allowing scientists to map the SAA and monitor its changes over time. According to the European Space Agency’s (ESA) website , the Swarm constellation is crucial for understanding our planet’s inner workings.
The Expansion | What the New Data Shows
Okay, so the SAA exists, we know it affects satellites, but why is everyone talking about this new data? Well, the Swarm satellite data indicates that the SAA isn’t just sitting there; it’s expanding. And not only is it expanding, but it also appears to be splitting into two lobes. This is a significant change, and scientists are working hard to understand why it’s happening.
One leading theory is that it’s related to changes in the Earth’s core. As the molten iron sloshes around deep inside our planet, it causes fluctuations in the magnetic field. These fluctuations can lead to the weakening and expansion of the SAA. It’s important to monitor the ionosphere for impacts too.
What fascinates me is that this expansion could have implications for satellite operations. As the SAA grows, more satellites will be exposed to higher levels of radiation, increasing the risk of malfunctions. This could lead to more frequent outages and potentially even damage to valuable space assets. What does that mean for us? Well, let’s just say your favorite streaming service might get a little glitchy sometimes. You can see details on this on the NASA website.
Is This a Sign of a Geomagnetic Reversal?
Now, here’s where things get a little more dramatic. One question that often comes up when discussing the SAA is whether it’s a sign of an impending geomagnetic reversal. A geomagnetic reversal is when the Earth’s magnetic north and south poles switch places. It’s happened many times throughout Earth’s history. According to the latest circular, the geomagnetic reversal doesn’t seem to be happening anytime soon.
The thing is, these reversals are typically slow processes, taking thousands of years to complete. While the weakening of the magnetic field in the SAA could be a precursor to a reversal, it’s not necessarily the case. Scientists are still studying the phenomenon, and more data is needed to draw any definitive conclusions. But, it’s something they’re keeping a close eye on. This process relies heavily on satellite data.
The latest data from Swarm satellites suggests that the SAA is indeed dynamic and changing. But , it also highlights the importance of continued monitoring and research. Understanding the SAA and its evolution is crucial for protecting our space assets and mitigating the potential risks associated with increased radiation exposure. And let’s be honest, keeping our satellites running smoothly is pretty important in today’s interconnected world.
FAQ About the South Atlantic Anomaly
What does the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) mean for the average person in India?
While you won’t directly feel the effects, disruptions to satellites passing through the SAA can indirectly impact services like GPS navigation and weather forecasting, which are increasingly important in our daily lives.
Could the South Atlantic Anomaly expansion affect air travel?
Potentially, yes. High-altitude flights over the SAA region might experience slightly increased radiation levels. However, the atmosphere still provides substantial protection.
Is the South Atlantic Anomaly a sign of the Earth’s poles flipping?
It could be a precursor, but it’s not a certainty. Geomagnetic reversals are slow processes, and more data is needed to determine if the SAA is related.
What are scientists doing to monitor the South Atlantic Anomaly?
Missions like the European Space Agency’s Swarm satellites are constantly gathering data on the Earth’s magnetic field to track the SAA’s changes and understand its causes.
If satellites malfunction, what happens?
Depending on the satellite’s use-case, satellite malfunctions can cause communication disruptions, less accurate weather predictions, and GPS errors.
How does the South Atlantic Anomaly expansion affect the magnetic field overall?
The magnetic field will weaken, and thus the radiation will increase.




